- Sep 8, 2014
- 25,420
- 59,319
I've never read the origins of how Amazon started, and Jeff Bezos back story. This is a good Cliff's Notes version from Mad Hedge Fund Trader (a blog I subscribe to). Regrettably, I only own 2 shares of Amazon (at a DCA of about $3k).
Why Amazon is Beating All
I believe there is a good chance that this creation of Jeff Bezos will see its shares double over the next five years.
Amazon is, in effect, taking over the world.
Jeff Bezos, born Jeff Jorgensen, is the son of an itinerant alcoholic circus clown and a low-level secretary in Albuquerque, New Mexico. When he was three, his father abandoned the family. His mother remarried a Cuban refugee, Miguel Bezos, who eventually became a chemical engineer for Exxon.
I have known Jeff Bezos for so long he had hair when we first met in the 1980s. He was a quantitative researcher in the bond department at Morgan Stanley, and I was the head of international trading.
Bezos was then recruited by the cutting-edge quantitative hedge fund, D.E. Shaw, which was making fortunes at the time, but nobody knew how. When I heard in 1994 that he left his certain success there to start an online bookstore, I thought he’d suffered a nervous breakdown, common in our industry.
Bezos incorporated his company in Washington state later that year, initially calling it “Cadabra” and then “Relentess.com.” He finally chose “Amazon” as the first interesting word that appeared in the dictionary, suggesting a river of endless supply. When I learned that Bezos would call his start-up “Amazon,” I thought he’d gone completely nuts.
Bezos funded his start-up with a $300,000 investment from his parents who he promised stood a 75% chance of losing their entire investment. But then his parents had already spent a lifetime running Bezos through a series of programs for gifted children, so they had the necessary confidence.
It was a classic garage start-up with three employees based in scenic Bellevue, Washington. The hours were long with all of the initial effort going into programming the initial site. To save money, Bezos bought second-hand pine doors which he placed on sawhorses, which stood in for proper desks.
Bezos initially considered 20 different industries to disrupt, including CDs and computer software. He quickly concluded that books were the ripest for disruption, as they were cheap, globally traded, and offered millions of titles.
When Amazon.com was finally launched in 1995, the day was spent fixing software bugs on the site, and the night wrapping and shipping the 50 or so orders a day. Growth was hyperbolic from the get-go, with sales reaching $20,000 a week by the end of the second month.
An early problem was obtaining supplies of books when wholesalers refused to offer him credit or deliver books on time. Eventually, he would ask suppliers to keep a copy of every book in existence at their own expense, which could ship within 24 hours.
Venture capital rounds followed, eventually raising $200 million. Early participants all became billionaires, gaining returns or 10,000-fold or more, including his trusting parents. There is one guy out there who missed becoming a billionaire because he didn’t check his voicemail often enough, which invited him into the initial funding round.
Bezos put the money to work, launching into a hiring binge of epic proportions. “Send us your freaks,” Bezos told the recruiting agencies, looking for the tattooed and the heavily pierced who were willing to work in shipping late at night for low wages. Keeping costs rock bottom was always an essential part of the Amazon formula.
Bezos used his new capital to raid Wal-Mart (WMT) for its senior distribution staff, for which it was later sued.
Amazon rode on the coattails of the Dotcom Boom to go public on NASDAQ on May 15, 1997 at $18 a share. The shares quickly rocketed to an astonishing $105, and in 1999 Jeff Bezos became Time magazine’s “Man of the Year.”
Unfortunately, the company committed many of the mistakes common to inexperienced management with too much cash on their hands. It blew $200 million on acquisitions that, for the most part, failed. Those include such losers as Pets.com and Drugstore.com. But Bezos’s philosophy has always been to try everything and fail them quickly, thus enabling Amazon to evolve 100 times faster than any other.
Amazon went into the Dotcom crash with tons of money on its hands, thus enabling it to survive the long funding drought that followed. Thousands of other competitors failed. Amazon shares plunged to $5.
But the company kept on making money. Sales soared by 50% a month, eventually topping $1 billion by 2001. The media noticed Wall Street took note. The company moved from the garage to a warehouse to a decrepit office building in downtown Seattle.
Amazon moved beyond books to compact disc sales in 1999. Electronics and toys followed. At its New York toy announcement, Bezos realized that the company actually had no toys on hand. So, he ordered an employee to max out his credit card cleaning out the local Hammacher Schlemmer just to obtain some convincing props.
A pattern emerged. As Bezos entered a new industry, he originally offered to run the online commerce for the leading firm. This happened with Circuit City, Borders, and Toys “R” Us. The firms then offered to take over Amazon, but Bezos wasn’t selling.
In the end Amazon came to dominate every field it entered. Please note that all three of the abovementioned firms no longer exist, thanks to extreme price competition from Amazon.
Amazon had a great subsidy in the early years as it did not charge state sales tax. As of 2011, it only charged sales tax in five states. That game is now over, with Amazon now collecting sales taxes in all 45 states that have them.
Amazon Web Services originally started out to manage the firm’s own website. It has since grown into a major profit center, with $17.4 billion in net revenues in 2017. Full disclosure: Mad Hedge Fund Trader is a customer.
Amazon entered the hardware business with the launch of its e-reader Kindle in 2007, which sold $5 billion worth in its first year. The Amazon Echo smart speaker followed in 2015 and boasts 71.9% market share. This is despite news stories that it records family conversations and randomly laughs.
Amazon Studios started in 2010, run by a former Disney executive, pumping out a series of high-grade film productions. In 2017 it became the first streaming studio to win an Oscar with Manchester by the Sea with Jeff Bezos visibly in the audience at the Hollywood awards ceremony.
Its acquisitions policy also became much more astute, picking up audiobook company Audible.com, shoe seller Zappos, Whole Foods, and most recently PillPack. Since its inception, Amazon has purchased more than 86 outside companies. Make that 89 with MGM Entertainment.
Sometimes, Amazon’s acquisition tactics are so predatory they would make John D. Rockefeller blush. It decided to get into the discount diaper business in 2010, and offered to buy Diapers.com, which was doing business under the name of “Quidsi.” The company refused, so Amazon began offering its own diapers for sale 30% cheaper for a loss. Diapers.com was driven to the wall and caved, selling out for $545 million. Diaper prices then popped back up to their original level.
Welcome to online commerce.
At the end of 2018, Amazon boasted some 306,000 employees worldwide. In fact, it has been the largest single job creator in the United States for the past decade. Also, this year it disclosed the number of Amazon Prime members at 100 million, then raised the price from $80 to $100, thus creating an instant $2 billion in profit.
The company’s ability to instantly create profit like this is breathtaking. And this will make you cry. In 2016, Amazon made $2.4 billion from Amazon gift cards left unredeemed!
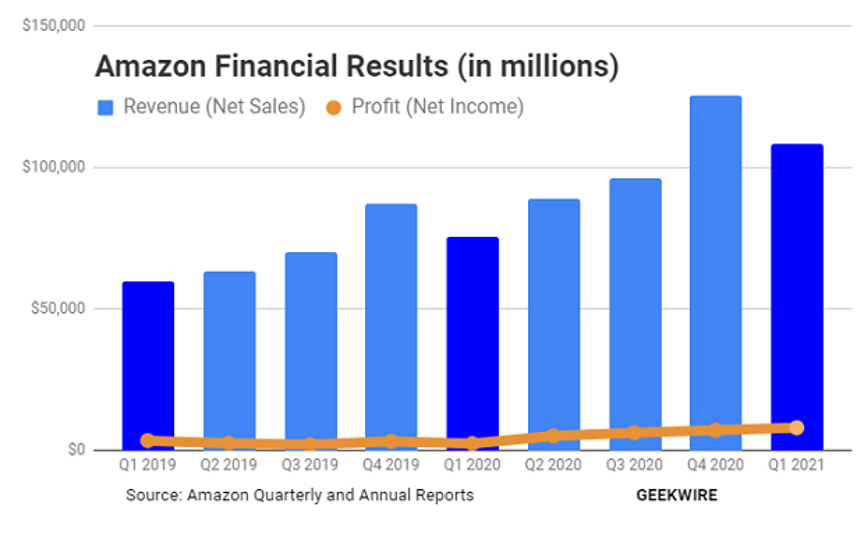
In Q1 of 2021, Amazon revenues totaled an unbelievable $108.5 billion, up 44% YOY. Both operating profits of $8.1 billion and operating margins of 8.2% set new records. It is currently capturing about 50% of all new online sales. Clearly, it was a huge pandemic winner.
So, what’s on the menu for Amazon? There is a lot of new ground to pioneer.
1) Healthcare is the big one, accounting for $3 trillion, or 17% of U.S. GDP, but where Amazon has just scratched the surface. Its recent $1 billion purchase of PillPack signals a new focus on the area. Who knows? The hyper-competition Bezos always brings to a new market would solve the American health care crisis, which is largely cost-driven. Bezos can oust middlemen like no one else.
2) Food is the great untouched market for online commerce, which accounts for 20% of total U.S. retail spending, but sees only 2% take place online. Essentially this is a distribution problem, and you have to accomplish this within the prevailing subterranean 1% profit margins in the industry. Books don’t need to be frozen or shipped fresh. Wal-Mart (WMT) will be target No. 1, which currently gets 56% of its sales from groceries. Amazon took a leap up the learnings curve with its $13.7 billion purchase of Whole Foods (WFC) in 2017. What will follow will be interesting.
3) Banking is another ripe area for “Amazonification,” where excessive fees are rampant. It would be easy for the company to accelerate the process through buying a major bank that already had licenses in all 50 states. Amazon is already working the credit card angle.
4) Overnight Delivery is a natural, as Amazon is already the largest shipper in the U.S., sending out more than 1 million packages a day. The company has a nascent effort here, already acquiring several aircraft to cover its most heavily trafficked routes. Expect FedEx (FDX), UPS (UPS), DHL, and the United States Post Office to get severely disrupted.
5) Clothing - Amazon has already surpassed Wal-Mart this year as the largest clothing retailer. The company has already launched 76 private labels, with half of them in the fashion area, such as Clifton Heritage (color and printed shirts), Buttoned Down (100% cotton shirts), and Goodthreads (casual shirts) as well as subscription services for all of the above.
6) Furniture is currently the fastest-growing category at Amazon. Customers can use an Amazon tool to design virtual rooms to see where new items and colors will fit best.
7) Event Ticketing firms like StubHub and Ticketmaster are among the most despised companies in the U.S., so they are great disruption candidates. Amazon has already started in the U.K., and a takeover of one of the above would ease its entry into the U.S.
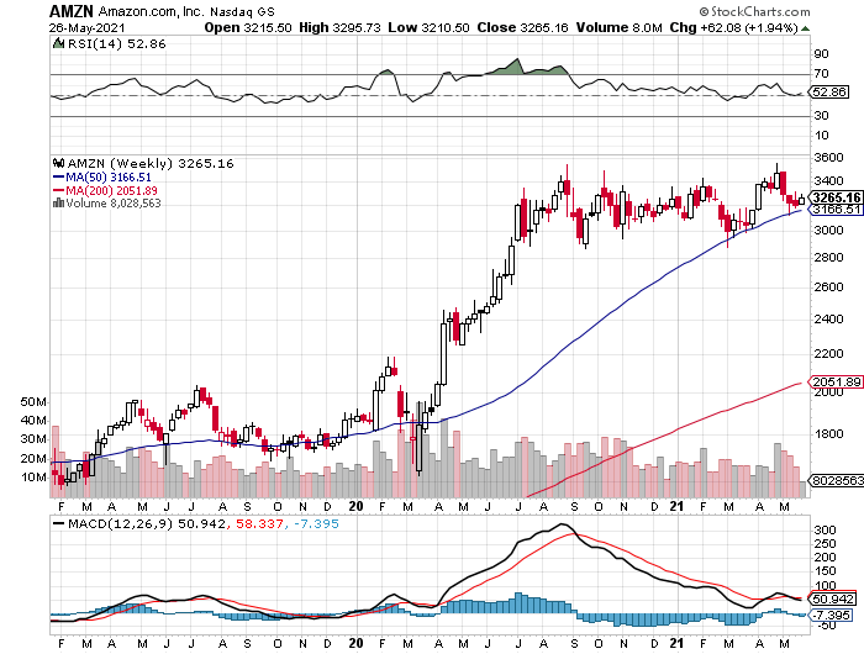
If only SOME of these new business ventures succeed, they have the potential to DOUBLE Amazon’s shares from current levels, taking its market capitalization up to $3.2 trillion. Perhaps this explains why institutional investors continue to pour into the shares, despite being up a torrid 134% from the February lows.
Whatever happened to Bezos’s real father, Ted Jorgensen? He was discovered by an enterprising journalist in 2012 running a bicycle shop in Glendale, Arizona. He had long ago sobered up and remarried. He had no idea who Jeff Bezos was. Ted Jorgensen died in 2015. Bezos never took the time to meet him. Too busy running Amazon, I guess. Worth over $200 billion, Bezos is now the second richest man in the world after Elon Musk.
Why Amazon is Beating All
I believe there is a good chance that this creation of Jeff Bezos will see its shares double over the next five years.
Amazon is, in effect, taking over the world.
Jeff Bezos, born Jeff Jorgensen, is the son of an itinerant alcoholic circus clown and a low-level secretary in Albuquerque, New Mexico. When he was three, his father abandoned the family. His mother remarried a Cuban refugee, Miguel Bezos, who eventually became a chemical engineer for Exxon.
I have known Jeff Bezos for so long he had hair when we first met in the 1980s. He was a quantitative researcher in the bond department at Morgan Stanley, and I was the head of international trading.
Bezos was then recruited by the cutting-edge quantitative hedge fund, D.E. Shaw, which was making fortunes at the time, but nobody knew how. When I heard in 1994 that he left his certain success there to start an online bookstore, I thought he’d suffered a nervous breakdown, common in our industry.
Bezos incorporated his company in Washington state later that year, initially calling it “Cadabra” and then “Relentess.com.” He finally chose “Amazon” as the first interesting word that appeared in the dictionary, suggesting a river of endless supply. When I learned that Bezos would call his start-up “Amazon,” I thought he’d gone completely nuts.
Bezos funded his start-up with a $300,000 investment from his parents who he promised stood a 75% chance of losing their entire investment. But then his parents had already spent a lifetime running Bezos through a series of programs for gifted children, so they had the necessary confidence.
It was a classic garage start-up with three employees based in scenic Bellevue, Washington. The hours were long with all of the initial effort going into programming the initial site. To save money, Bezos bought second-hand pine doors which he placed on sawhorses, which stood in for proper desks.
Bezos initially considered 20 different industries to disrupt, including CDs and computer software. He quickly concluded that books were the ripest for disruption, as they were cheap, globally traded, and offered millions of titles.
When Amazon.com was finally launched in 1995, the day was spent fixing software bugs on the site, and the night wrapping and shipping the 50 or so orders a day. Growth was hyperbolic from the get-go, with sales reaching $20,000 a week by the end of the second month.
An early problem was obtaining supplies of books when wholesalers refused to offer him credit or deliver books on time. Eventually, he would ask suppliers to keep a copy of every book in existence at their own expense, which could ship within 24 hours.
Venture capital rounds followed, eventually raising $200 million. Early participants all became billionaires, gaining returns or 10,000-fold or more, including his trusting parents. There is one guy out there who missed becoming a billionaire because he didn’t check his voicemail often enough, which invited him into the initial funding round.
Bezos put the money to work, launching into a hiring binge of epic proportions. “Send us your freaks,” Bezos told the recruiting agencies, looking for the tattooed and the heavily pierced who were willing to work in shipping late at night for low wages. Keeping costs rock bottom was always an essential part of the Amazon formula.
Bezos used his new capital to raid Wal-Mart (WMT) for its senior distribution staff, for which it was later sued.
Amazon rode on the coattails of the Dotcom Boom to go public on NASDAQ on May 15, 1997 at $18 a share. The shares quickly rocketed to an astonishing $105, and in 1999 Jeff Bezos became Time magazine’s “Man of the Year.”
Unfortunately, the company committed many of the mistakes common to inexperienced management with too much cash on their hands. It blew $200 million on acquisitions that, for the most part, failed. Those include such losers as Pets.com and Drugstore.com. But Bezos’s philosophy has always been to try everything and fail them quickly, thus enabling Amazon to evolve 100 times faster than any other.
Amazon went into the Dotcom crash with tons of money on its hands, thus enabling it to survive the long funding drought that followed. Thousands of other competitors failed. Amazon shares plunged to $5.
But the company kept on making money. Sales soared by 50% a month, eventually topping $1 billion by 2001. The media noticed Wall Street took note. The company moved from the garage to a warehouse to a decrepit office building in downtown Seattle.
Amazon moved beyond books to compact disc sales in 1999. Electronics and toys followed. At its New York toy announcement, Bezos realized that the company actually had no toys on hand. So, he ordered an employee to max out his credit card cleaning out the local Hammacher Schlemmer just to obtain some convincing props.
A pattern emerged. As Bezos entered a new industry, he originally offered to run the online commerce for the leading firm. This happened with Circuit City, Borders, and Toys “R” Us. The firms then offered to take over Amazon, but Bezos wasn’t selling.
In the end Amazon came to dominate every field it entered. Please note that all three of the abovementioned firms no longer exist, thanks to extreme price competition from Amazon.
Amazon had a great subsidy in the early years as it did not charge state sales tax. As of 2011, it only charged sales tax in five states. That game is now over, with Amazon now collecting sales taxes in all 45 states that have them.
Amazon Web Services originally started out to manage the firm’s own website. It has since grown into a major profit center, with $17.4 billion in net revenues in 2017. Full disclosure: Mad Hedge Fund Trader is a customer.
Amazon entered the hardware business with the launch of its e-reader Kindle in 2007, which sold $5 billion worth in its first year. The Amazon Echo smart speaker followed in 2015 and boasts 71.9% market share. This is despite news stories that it records family conversations and randomly laughs.
Amazon Studios started in 2010, run by a former Disney executive, pumping out a series of high-grade film productions. In 2017 it became the first streaming studio to win an Oscar with Manchester by the Sea with Jeff Bezos visibly in the audience at the Hollywood awards ceremony.
Its acquisitions policy also became much more astute, picking up audiobook company Audible.com, shoe seller Zappos, Whole Foods, and most recently PillPack. Since its inception, Amazon has purchased more than 86 outside companies. Make that 89 with MGM Entertainment.
Sometimes, Amazon’s acquisition tactics are so predatory they would make John D. Rockefeller blush. It decided to get into the discount diaper business in 2010, and offered to buy Diapers.com, which was doing business under the name of “Quidsi.” The company refused, so Amazon began offering its own diapers for sale 30% cheaper for a loss. Diapers.com was driven to the wall and caved, selling out for $545 million. Diaper prices then popped back up to their original level.
Welcome to online commerce.
At the end of 2018, Amazon boasted some 306,000 employees worldwide. In fact, it has been the largest single job creator in the United States for the past decade. Also, this year it disclosed the number of Amazon Prime members at 100 million, then raised the price from $80 to $100, thus creating an instant $2 billion in profit.
The company’s ability to instantly create profit like this is breathtaking. And this will make you cry. In 2016, Amazon made $2.4 billion from Amazon gift cards left unredeemed!
In Q1 of 2021, Amazon revenues totaled an unbelievable $108.5 billion, up 44% YOY. Both operating profits of $8.1 billion and operating margins of 8.2% set new records. It is currently capturing about 50% of all new online sales. Clearly, it was a huge pandemic winner.
So, what’s on the menu for Amazon? There is a lot of new ground to pioneer.
1) Healthcare is the big one, accounting for $3 trillion, or 17% of U.S. GDP, but where Amazon has just scratched the surface. Its recent $1 billion purchase of PillPack signals a new focus on the area. Who knows? The hyper-competition Bezos always brings to a new market would solve the American health care crisis, which is largely cost-driven. Bezos can oust middlemen like no one else.
2) Food is the great untouched market for online commerce, which accounts for 20% of total U.S. retail spending, but sees only 2% take place online. Essentially this is a distribution problem, and you have to accomplish this within the prevailing subterranean 1% profit margins in the industry. Books don’t need to be frozen or shipped fresh. Wal-Mart (WMT) will be target No. 1, which currently gets 56% of its sales from groceries. Amazon took a leap up the learnings curve with its $13.7 billion purchase of Whole Foods (WFC) in 2017. What will follow will be interesting.
3) Banking is another ripe area for “Amazonification,” where excessive fees are rampant. It would be easy for the company to accelerate the process through buying a major bank that already had licenses in all 50 states. Amazon is already working the credit card angle.
4) Overnight Delivery is a natural, as Amazon is already the largest shipper in the U.S., sending out more than 1 million packages a day. The company has a nascent effort here, already acquiring several aircraft to cover its most heavily trafficked routes. Expect FedEx (FDX), UPS (UPS), DHL, and the United States Post Office to get severely disrupted.
5) Clothing - Amazon has already surpassed Wal-Mart this year as the largest clothing retailer. The company has already launched 76 private labels, with half of them in the fashion area, such as Clifton Heritage (color and printed shirts), Buttoned Down (100% cotton shirts), and Goodthreads (casual shirts) as well as subscription services for all of the above.
6) Furniture is currently the fastest-growing category at Amazon. Customers can use an Amazon tool to design virtual rooms to see where new items and colors will fit best.
7) Event Ticketing firms like StubHub and Ticketmaster are among the most despised companies in the U.S., so they are great disruption candidates. Amazon has already started in the U.K., and a takeover of one of the above would ease its entry into the U.S.
If only SOME of these new business ventures succeed, they have the potential to DOUBLE Amazon’s shares from current levels, taking its market capitalization up to $3.2 trillion. Perhaps this explains why institutional investors continue to pour into the shares, despite being up a torrid 134% from the February lows.
Whatever happened to Bezos’s real father, Ted Jorgensen? He was discovered by an enterprising journalist in 2012 running a bicycle shop in Glendale, Arizona. He had long ago sobered up and remarried. He had no idea who Jeff Bezos was. Ted Jorgensen died in 2015. Bezos never took the time to meet him. Too busy running Amazon, I guess. Worth over $200 billion, Bezos is now the second richest man in the world after Elon Musk.




